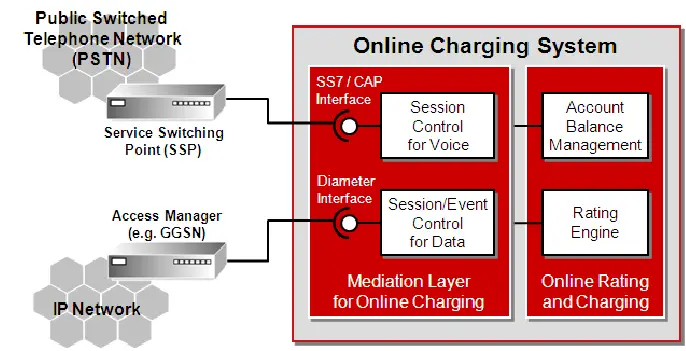
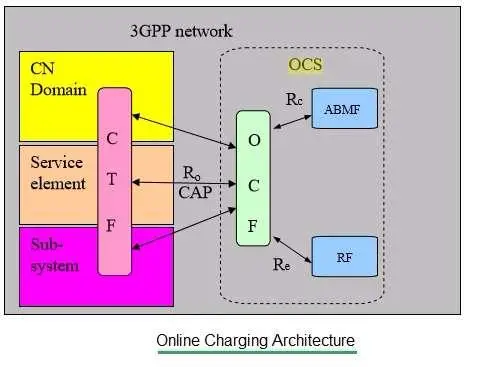
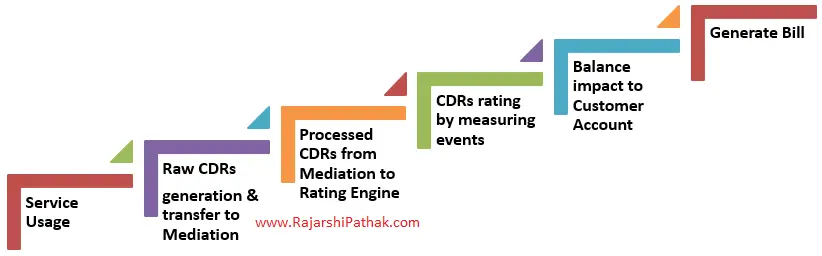
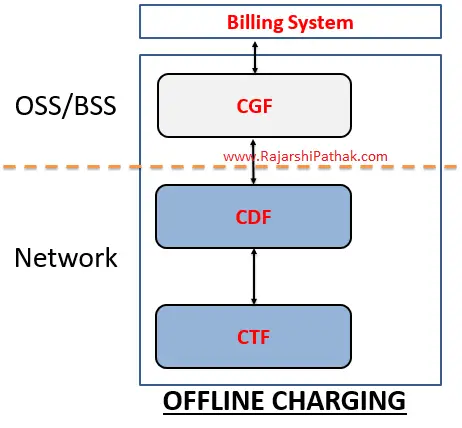
Medical organizations are the main force behind humanity’s efforts to change the tide in the battle against the infamous sickness as COVID-19 is not loosening its grip on the world. Hospitals and research facilities are more vulnerable to malware invasions than ever before because they are overrun with work that saves lives. However, cybercriminals don’t exhibit the necessary sympathy. Some of them keep focusing on the healthcare industry as if it weren’t the new reality in light of the pandemic.
One of the most repulsive cybercrime trends of 2020 is the increase in phishing campaigns based on the coronavirus panic. Users are being tricked into divulging their account passwords and installing banking Trojans by rogue emails that imitate reputable medical organizations, like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Even though these scams are not only targeted at the healthcare sector, ransomware nevertheless rears its ugly head by specifically attacking hospital computer networks.
A RISK THAT IS RAISING
Hospitals are increasingly being targeted with ransomware attacks, according to the International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol). The aftermath of such an attack is not limited to data effect, as the officials heavily emphasize. It makes it more difficult to respond quickly to medical emergencies, which could have major real-world repercussions and put many patients at danger.
Interpol sent a Purple Notice to law enforcement organizations in each of its 194 member nations due to the rising ransomware activity that is harming this industry. By soliciting information from the public about criminal strategies, techniques, and procedures, the organization hopes to raise general awareness of the issue (TTP).
In addition, Interpol promises member nations that it will make every effort to offer the required technical assistance and threat reduction services. Its Cyber Threat Response (CTR) section is also gathering data on malicious web domains serving as ransomware delivery systems.
In terms of prevention, the organization reaffirms that emails with hazardous attachments or hyperlinks leading to harmful payloads are the main means by which ransomware is spread. That being said, the most important piece of advice is to make sure that staff members can spot a phishing attack and stay out of trouble.
Additionally, healthcare providers should prioritize their data and keep the most crucial documents apart from the rest of their information. Furthermore, it will be much more difficult for intruders to access your system if you regularly update your software, use trustworthy anti-malware solutions, and use strong passwords or two-factor authentication (2FA).
Ryuk Ransomware continues to take advantage of hospitals.
Despite the crisis, Ryuk, an enterprise-targeting ransomware operation, is still infecting hospitals. In March 2020, one of these attacks was discovered by security experts. They discovered that the thieves had contaminated the digital infrastructure of an unnamed American health organization using the remote execution application PsExec.
On infected systems, the predatory application encrypted crucial data and generated ransom letters.
SentinelOne, a security company, discovered a coordinated campaign around the same time in which Ryuk operators attempted to attack numerous COVID-19 response facilities all around the United States. Their prominent targets were a network of nine hospitals as well as two independent clinics.
DHARMA RANSOMWARE follows a similar route.
The notorious Dharma ransomware family is still waging damaging attacks against hospitals in the midst of the coronavirus catastrophe. It made its debut in 2016 as a threat aimed at individuals before being modified to target business networks.
The COVID-19 theme is utilized in numerous ways by one of the most recent Dharma variations. It makes use of a binary file called 1covid.exe that appears to be a secure email attachment. When an unwary victim opens this file, the ransomware infects the computer and starts a post-exploitation scenario to try to infect other devices connected to the same network.
The organization’s files are then encrypted using a combination of the RSA and AES cryptographic techniques. It’s interesting that coronavirus@qq.com is provided as the contact email address in the ransom note. The ransom fee can be a few to tens of bitcoins, depending on the size of the hacked network.
Russian criminals stalk European pharmaceutical companies
Pharma firms with headquarters in Germany and Belgium experienced extortion attacks in January 2020, which were coordinated by two hacker organizations. Russian-speaking cyber criminal gangs nicknamed Silence and TA505, according to analysts from security services company Group-IB, were in charge of these incidents. While the former had been active in attacking the healthcare sector, Silence had concentrated on compromising financial institutions and changed its strategy abruptly when the epidemic started.
According to reports, both gangs entered the targets’ networks via privilege escalation flaws identified as CVE-2019-1322 and CVE-2019-1405, respectively. Fortunately, the assaults were discovered and stopped before they could cause any harm.
The attacks were probably ransomware operations disguising themselves as data breaches, according to Group-IB analysts, despite the fact that the hackers were unable to run their code. The white hats underline that the TA505 crew is known to have employed ransom Trojans in the past, including Rapid and Locky, as part of their justification.
FEELINGS FROM SOME THREATENING ACTORS
Several ransomware gangs assert that they are ceasing attacks on hospitals, in contrast to the mischief outlined in the preceding paragraphs. Experts from the BleepingComputer security resource made contact with the perpetrators of widespread cyber-extortion activities in March 2020. Finding out if the bad guys intended to flee the medical scene in light of the coronavirus emergency was the study team’s main objective.
Unbelievably, some of the addressees have responded, according to the analysts. Hospitals and humanitarian organizations were never among the targets of the Clop ransomware, according to its creators, and this won’t change. Even if such an institution unintentionally becomes compromised, the criminals will allegedly send it a decryption tool without any conditions.
However, the villains claimed that they did not view companies in the pharmaceutical industry as deserving of their pity. The explanation is that because these businesses are thriving in the midst of the pandemic, they would be forced to make restitution if attacked.
Another ongoing ransomware strain, DoppelPaymer, was created by people who allegedly followed suit. In their response, they said that if a hospital ended up on their hook, they would immediately decrypt its files. However, the victim is required to submit proof that it is a healthcare professional in order to be qualified for such treatment. Similar to Clop, this syndicate won’t compromise on the ransom demands from pharmaceutical corporations.
The cybercriminal organizations who created the ransomware strains known as NetWalker and Nefilim claimed they had never explicitly targeted hospitals or nonprofits and had no plans to do so. However, there is a catch: If a healthcare institution falls victim to accidental entrapment, NetWalker will demand a ransom.
The creators of Maze, a type of ransomware that exploits data stolen from victims before encryption to put further pressure on victims, said they wouldn’t attack hospital computer networks until the pandemic was ended. They must have had a poker face on when they wrote their response, though. Why? Read on. Soon after making their threat, they released documents taken from Hammersmith Medicines Research, a company testing COVID-19 vaccines, which was attacked. This information includes the personal files of many previous patients.
More than a thousand patients of the Montana VA Health Care System, which provides services to veterans, had their private information exposed by Maze in June 2020. The initial assault happened in late April, and the criminals turned their wrath on the victimized group that refused to pay the ransom. What lesson does the tale teach us? For these dishonest scoundrels, ethics is a meaningless concept.
THE CONCLUSION
The globe is seeing unusual conditions that combine online threats and physical dangers into an odd whole. Never before has the reliability of electronic systems been so crucial to people’s lives. Ransomware creators are displaying their true selves during these difficult times. By attacking vital healthcare infrastructure and restricting access to hospital databases, they obstruct timely medical assistance in situations where seconds can make all the difference.
Although some extortion gangs have allegedly stopped attacking hospitals, it is risky to place too much faith in their assurances at this time. Instead, the healthcare sector should concentrate on fortifying its defenses and proactively repelling ransomware raids.
All important data must first and foremost be backed up. Additionally, security awareness training for the staff is crucial to these remedies because most ransomware cases begin with an employee blunder in which they open an alluring email attachment. It’s important to use 2FA or difficult-to-guess passwords for proper account sign-in hygiene. Additionally, a powerful anti-malware programme should be able to recognise all common varieties of ransomware and stop them before they cause damage.
Related Tags: security, awareness, healthcare, ransomeware, antimalware, threats, pharmaceutical, cybercriminal, risk